Icse Question answers Numerical Reflection light
- Angle of Incidence
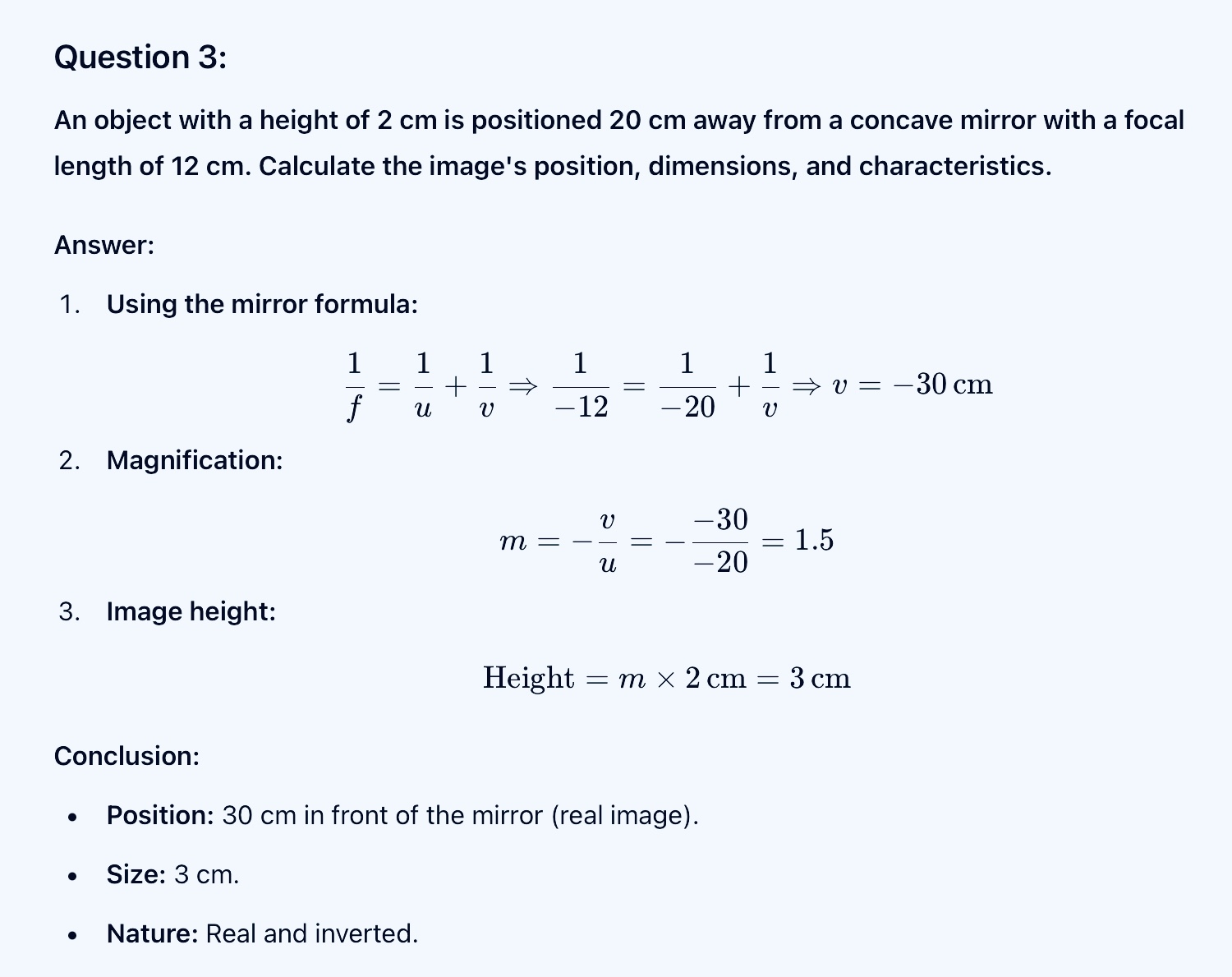
Question: A light ray strikes a plane mirror, and the angle between the incident ray and the reflected ray is 90 degrees. What is the angle of incidence?
Answer: If the angle between the incident ray and the reflected ray is 90 degrees,
we can denote the angle of incidence as i and the angle of reflection as r.
According to the law of reflection:
i+r=90°
Since
i=r,
we can express it as:
i+i=90°
2i=90°
I=45°
Thus, the angle of incidence is 45 degrees.
- Distance from the Mirror
Question: A person stands in front of a plane mirror and observes their reflection at a distance of 10 meters from them. How far is the person standing from the mirror?
Answer: In a plane mirror, the image is located the same distance behind the mirror as the object is in front of it. If the total distance to the image is 10 meters, we can set:
Distance from the person to the mirror = d meters
Distance from the mirror to the image = d meters.
This gives us the equation:
d+d=10
2d=10
d=5 meters.
Therefore, the person is standing 5 meters from the mirror.
If an object is positioned between two plane mirrors that are at a 90° angle to each other, how many distinct images will be formed?

When an object is placed between two plane mirrors inclined at 60°, how many images can be observed?

4. Two plane mirrors are placed at an angle of 50° to each other. If an object is positioned asymmetrically between them, how many distinct images of the object can be observed?
Question 1:
What is the focal length of a convex mirror with a radius of curvature of 40 cm?

Question 2:
What is the radius of curvature of a concave mirror with a focal length of 10 cm?

Question 3:
An object with a height of 2 cm is positioned 20 cm away from a concave mirror that has a focal length of 12 cm. Calculate the image’s position, dimensions, and characteristics.

Question 1:
An object is placed 4 cm in front of a concave mirror with a radius of curvature of 24 cm. Determine the location of the image and whether it is enlarged.
Question 2:
At what distance should an object be positioned from a concave mirror that has a focal length of 25 cm to ensure the image produced is the same size as the object?

Question 3:
A 5 cm tall object is placed 60 cm away from a concave mirror with a focal length of 10 cm. Calculate (i) the position and (ii) the dimensions of the resulting image.
Question 4:
A point light source is positioned 40 cm from a convex mirror with a focal length of 40 cm. Where will the image be located?
Question 5:
When a 1 cm tall object is positioned 4 cm away from a concave mirror, it creates an erect image that measures 1.5 cm and is located 6 cm behind the mirror. Find the focal length?
Question 6:
An object with a height of 4 cm is placed 30 cm in front of a concave mirror with a focal length of 15 cm. (a) At what location will the image appear? (b) How large will the image be?
Question 7:
A concave mirror creates a real image of an object placed 30 cm from it, where the image is three times larger than the object. Determine (a) the focal length of the mirror and (b) the location of the image.
Question 8:
When a concave mirror forms a virtual image that is twice the size of an object positioned 5 cm away, find (a) the focal length of the mirror and (b) the location of the image.
Question 9:
In the case of a convex mirror, if the image produced is one-third the size of the object, how do the object distance (u) and image distance (v) relate to each other?

Question 10:
If a concave mirror generates an erect image that is double the height of the object, what relationship exists between the object distance (u) and image distance (v)?

Question 11:
When the magnification of a mirror is -3, how are the object distance (u) and image distance (v) related?





