Complete Guide to CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 1: Matter in Our Surroundings – English+ हिन्दी Notes, Explanation, Key Questions & Concepts by Grandmaster Bikram Sutradhar

Complete Guide to CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 1: Matter in Our Surroundings – English+Hindi Notes, Explanation, Key Questions & Concepts by Grandmaster Bikram Sutradhar (SirBikramSutradhar)
SirBikramSutradhar
🏷️
SirBikramSutradhar class 9 cbse हिन्दी and English medium bAstronautWay class 9 Science ncert solution हिन्दी and English medium
📄
Unlock the secrets of Chapter 1 – Matter in Our Surroundings with this complete guide for CBSE Class 9 Science. Curated by Grandmaster Bikram Sutradhar (SirBikramSutradhar),
this article offers crystal-clear explanations, concept maps, solved examples, diagrams, key questions, and expert tips. Perfect for students aiming for top marks in exams. Understand states of matter, evaporation, changes in states, and much more in the simplest way possible!
Introduction
Detailed Notes
Diagrams
Important Questions
Mind Maps
Summary & Quick Revision
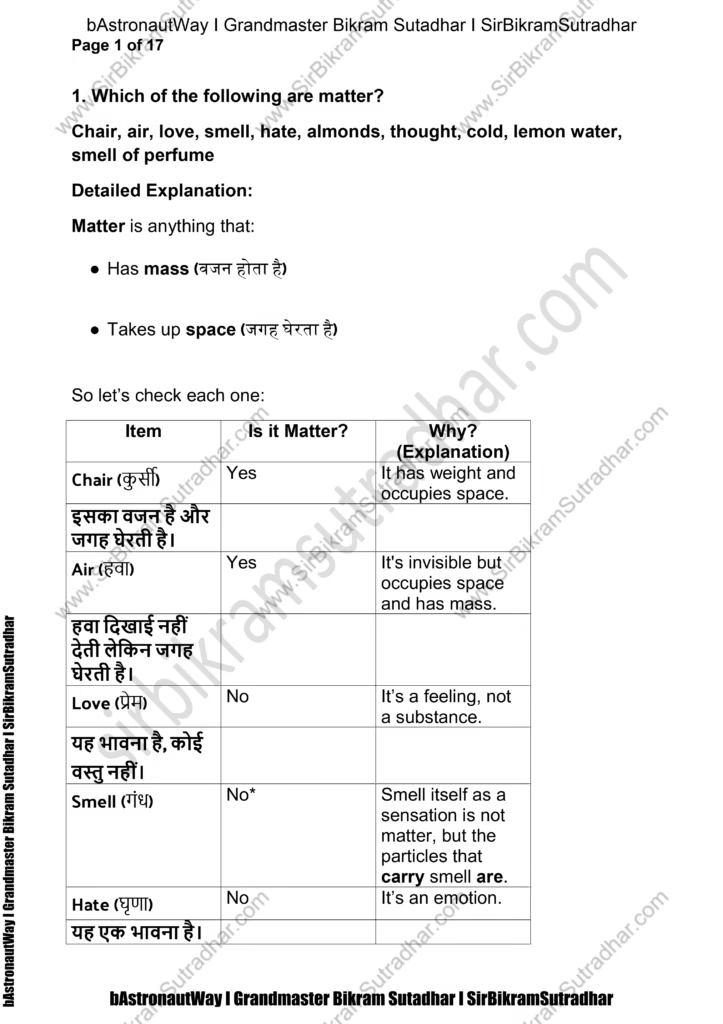
Which of the following are matter?
Chair, air, love, smell, hate, almonds, thought, cold, lemon water, smell of perfume
Detailed Explanation:
Matter is anything that:
● Has mass (वजन होता है)
● Takes up space (जगह घेरता है)
So let’s check each one:
Item Is it Matter? Why? (Explanation)
Chair (कुर्सी) Yes It has weight and occupies space.
इसका वजन है और जगह घेरती है।
Air (हवा) Yes It’s invisible but occupies space and has mass.
हवा दिखाई नहीं देती लेकिन जगह घेरती है।
Love (प्रेम) No It’s a feeling, not a substance.
यह भावना है, कोई वस्तु नहीं।
Smell (गंध) No* Smell itself as a sensation is not matter, but the particles that carry smell are.
Hate (घृणा) No It’s an emotion.
यह एक भावना है।
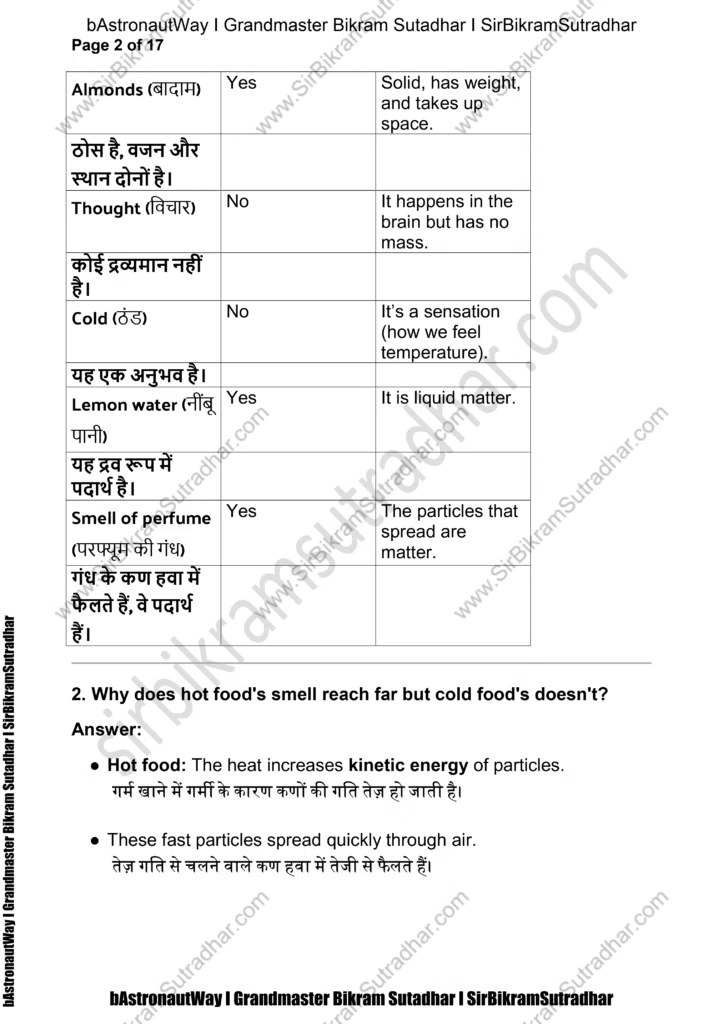
Almonds (बादाम) Yes Solid, has weight, and takes up space.
ठोस है, वजन और स्थान दोनों है।
Thought (विचार) No It happens in the brain but has no mass.
कोई द्रव्यमान नहीं है।
Cold (ठंड) No It’s a sensation (how we feel temperature).
यह एक अनुभव है।
Lemon water (नींबू पानी) Yes It is liquid matter.
यह द्रव रूप में पदार्थ है।
Smell of perfume (परफ्यूम की गंध) Yes The particles that spread are matter.
गंध के कण हवा में फैलते हैं, वे पदार्थ हैं।
- Why does hot food’s smell reach far but cold food’s doesn’t?
Answer:
● Hot food: The heat increases kinetic energy of particles.
गर्म खाने में गर्मी के कारण कणों की गति तेज़ हो जाती है।
● These fast particles spread quickly through air.
तेज़ गति से चलने वाले कण हवा में तेजी से फैलते हैं।
● That’s why we can smell hot food from a distance.
इसीलिए गरम खाने की खुशबू दूर से आती है।
● Cold food: Particles move slowly and don’t spread far.
ठंडे खाने में कण धीरे चलते हैं, इसलिए गंध पास से ही आती है।
Scientific Concept: This is due to diffusion – the movement of particles from high concentration to low concentration.
यह प्रक्रिया ‘प्रसरण’ (diffusion) कहलाती है।
-
📘 Becoming an Astronaut in India (ISRO) – A Complete Guide After Class 12
📘 Becoming an Astronaut in India (ISRO) – A Complete Guide After Class 12 ✍️…
-
Top 20 Shubh Tracks You MUST Watch on @SHUBHWORLDWIDE 🎧
Top 20 Shubh Tracks You MUST Watch on @SHUBHWORLDWIDE 🎧 📝 Top 20 Shubh Tracks…
-
🌟🎉 Anupa Datta Shines Again with 475 Marks in TBSE Class 12 Science 2025 – A True Inspiration! Tbse Board Result 2025 🎉🌟
📅 Published on: April 30, 2025📍 Agartala, Tripura In a world where challenges often dim…
-
🚀 bAstronautWay – Your Ultimate Learning Destination! 🎓✨
TBSE CBSE Undergraduate and Postgraduate Entrance Exams 📍 Our Locations: 9863002294 / 7005561197 📚 Courses…
-
9 Powerful Achievements of Sandeep Kumar: The Fearless Journey of India’s Race Walking Warrior
Who Is Sandeep Kumar? Sandeep Kumar is one of India’s most resilient and hardworking athletes…
-
11 Inspiring Facts About Siddharth Choudhary – Who Is India’s Rising Shot Put Record Holder
Siddharth Choudhary 1. Who Is Siddharth Choudhary? – India’s Emerging Shot Put Talent Siddharth Choudhary…
-
15 Inspiring Achievements of Pooja Kadian – India’s First Woman Wushu World Champion Who Created History
Pooja Kadian Introduction India has produced many remarkable athletes in combat sports, but Pooja Kadian…




-

9 Powerful Achievements of Sandeep Kumar: The Fearless Journey of India’s Race Walking Warrior
-

11 Inspiring Facts About Siddharth Choudhary – Who Is India’s Rising Shot Put Record Holder
-

15 Inspiring Achievements of Pooja Kadian – India’s First Woman Wushu World Champion Who Created History
-

10 Powerful Lessons from the Inspiring Journey of Yogesh Gamish Pawara – From Village Dreams to Rising Kho Kho Star






-
📘 Becoming an Astronaut in India (ISRO) – A Complete Guide After Class 12

📘 Becoming an Astronaut in India (ISRO) – A Complete Guide After Class 12 ✍️…
-
Top 20 Shubh Tracks You MUST Watch on @SHUBHWORLDWIDE 🎧

Top 20 Shubh Tracks You MUST Watch on @SHUBHWORLDWIDE 🎧 📝 Top 20 Shubh Tracks…
-
🌟🎉 Anupa Datta Shines Again with 475 Marks in TBSE Class 12 Science 2025 – A True Inspiration! Tbse Board Result 2025 🎉🌟

📅 Published on: April 30, 2025📍 Agartala, Tripura In a world where challenges often dim…
-
🚀 bAstronautWay – Your Ultimate Learning Destination! 🎓✨

TBSE CBSE Undergraduate and Postgraduate Entrance Exams 📍 Our Locations: 9863002294 / 7005561197 📚 Courses…
-
9 Powerful Achievements of Sandeep Kumar: The Fearless Journey of India’s Race Walking Warrior

Who Is Sandeep Kumar? Sandeep Kumar is one of India’s most resilient and hardworking athletes…
-
11 Inspiring Facts About Siddharth Choudhary – Who Is India’s Rising Shot Put Record Holder

Siddharth Choudhary 1. Who Is Siddharth Choudhary? – India’s Emerging Shot Put Talent Siddharth Choudhary…
-
15 Inspiring Achievements of Pooja Kadian – India’s First Woman Wushu World Champion Who Created History

Pooja Kadian Introduction India has produced many remarkable athletes in combat sports, but Pooja Kadian…




- A diver cuts through water – which property of matter does it show?
Answer:
● Water particles are not tightly packed.
पानी के कण बहुत पास-पास नहीं होते।
● So, a diver can move through the gaps.
इसलिए गोताखोर उन खाली जगहों से होकर तैर सकता है।
This also shows that liquids can flow and take shape of container.
यह भी बताता है कि द्रव (liquid) बह सकते हैं और बर्तन का आकार ले सकते हैं।
- Characteristics of Particles of Matter
पदार्थ के कणों की विशेषताएँ:
Let’s go point-by-point: - Particles are very small
कण बहुत छोटे होते हैं।
We can’t see them with the naked eye, but they exist.
हम उन्हें सीधे नहीं देख सकते, पर वे होते हैं। - Particles have space between them
कणों के बीच खाली स्थान होता है।
In gases, the space is more; in solids, less.
गैस में सबसे ज़्यादा, ठोस में सबसे कम। - Particles are constantly moving
कण लगातार गति करते रहते हैं।
Even in solids, they vibrate.
ठोस में भी कण कंपन करते हैं। - Particles attract each other
कण एक-दूसरे को आकर्षित करते हैं।
This force is strongest in solids, weakest in gases.
ठोस में यह बल सबसे ज्यादा होता है।
- The mass per unit volume of a substance is called density.
(density = mass/volume)
घनत्व = द्रव्यमान / आयतन
एक पदार्थ का प्रति इकाई आयतन में जितना द्रव्यमान होता है, उसे घनत्व कहते हैं।
:
air, exhaust from chimneys, honey, water, chalk, cotton, iron
(घटते से बढ़ते घनत्व के क्रम में लगाइए)
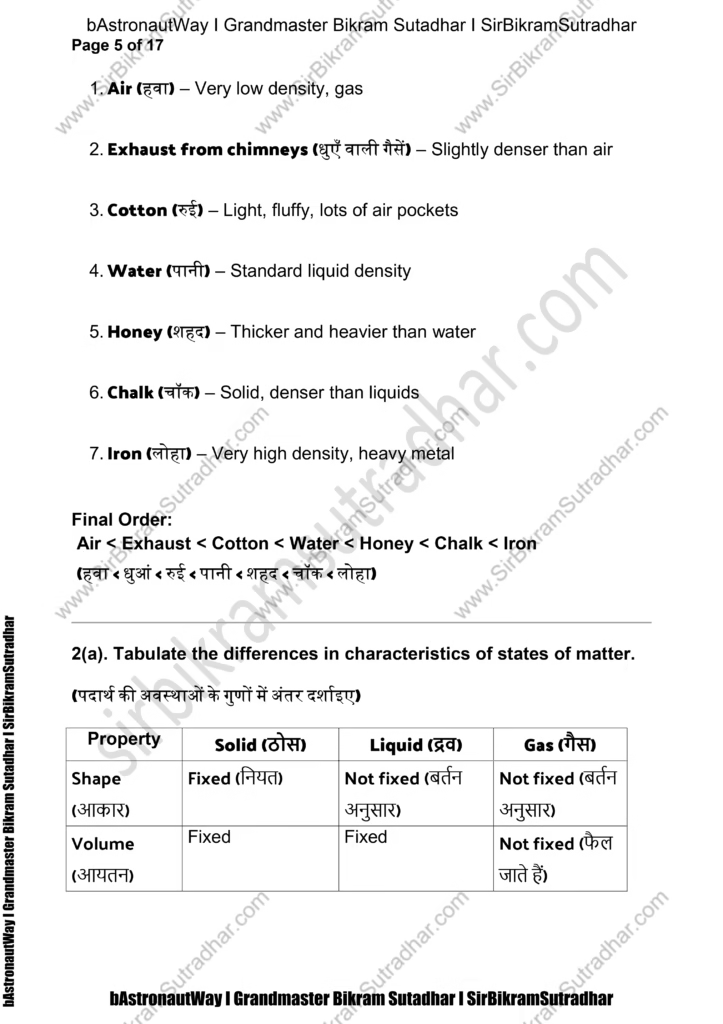
Answer (from least to greatest density): - Air (हवा) – Very low density, gas
- Cotton (रुई) – Light, fluffy, lots of air pockets
- Water (पानी) – Standard liquid density
- Honey (शहद) – Thicker and heavier than water
- Iron (लोहा) – Very high density, heavy metal
Final Order:
(हवा < धुआं < रुई < पानी < शहद < चॉक < लोहा)
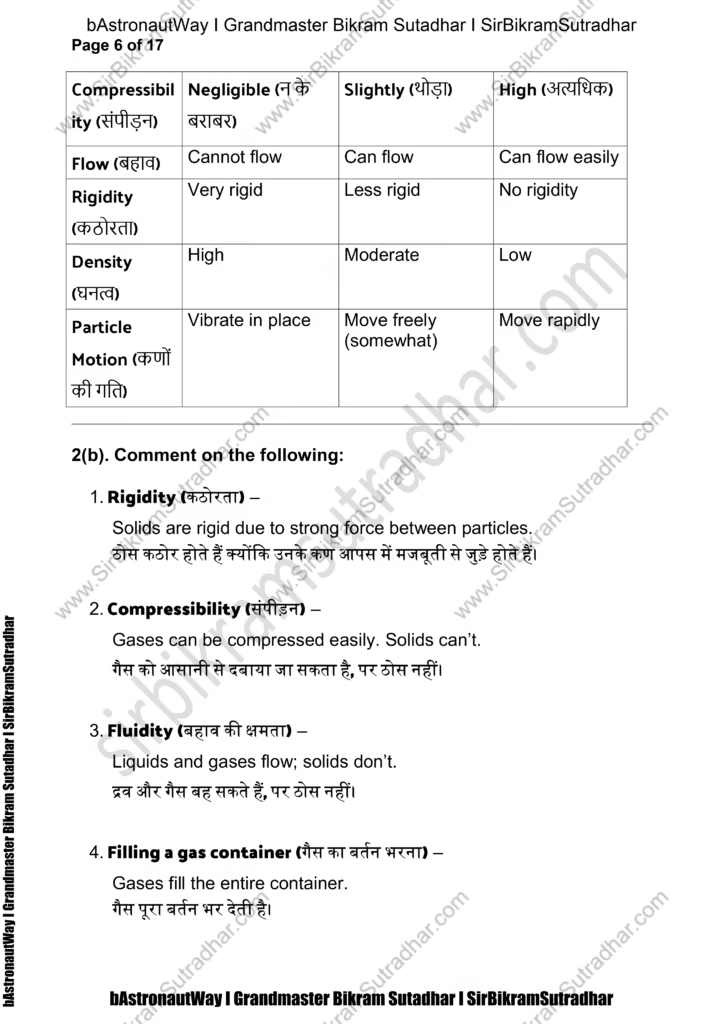
2(a). Tabulate the differences in characteristics of states of matter.
(पदार्थ की अवस्थाओं के गुणों में अंतर दर्शाइए)
Property Solid (ठोस) Liquid (द्रव) Gas (गैस)
Shape (आकार) Fixed (नियत) Not fixed (बर्तन अनुसार) Not fixed (बर्तन अनुसार)
Volume (आयतन) Fixed Fixed Not fixed (फैल जाते हैं)
Compressibility (संपीड़न) Negligible (न के बराबर) Slightly (थोड़ा) High (अत्यधिक)
Flow (बहाव) Cannot flow Can flow Can flow easily
Rigidity (कठोरता) Very rigid Less rigid No rigidity
Density (घनत्व) High Moderate Low
Particle Motion (कणों की गति) Vibrate in place Move freely (somewhat) Move rapidly
2(b). Comment on the following:
- Rigidity (कठोरता) –
Solids are rigid due to strong force between particles.
ठोस कठोर होते हैं क्योंकि उनके कण आपस में मजबूती से जुड़े होते हैं। - Compressibility (संपीड़न) –
Gases can be compressed easily. Solids can’t.
गैस को आसानी से दबाया जा सकता है, पर ठोस नहीं। - Fluidity (बहाव की क्षमता) –
Liquids and gases flow; solids don’t.
द्रव और गैस बह सकते हैं, पर ठोस नहीं। - Filling a gas container (गैस का बर्तन भरना) –
Gases fill the entire container.
गैस पूरा बर्तन भर देती है। - Shape (आकार) –
Solids have fixed shape, others take the container’s shape.
ठोस का निश्चित आकार होता है, बाकी बर्तन के अनुसार। - Kinetic energy (गतिक ऊर्जा) –
Gases > Liquids > Solids
गैसों में सबसे ज्यादा, फिर द्रव, फिर ठोस में सबसे कम। - Density (घनत्व) –
Solids have highest, gases have least.
ठोस में सबसे अधिक, गैस में सबसे कम।
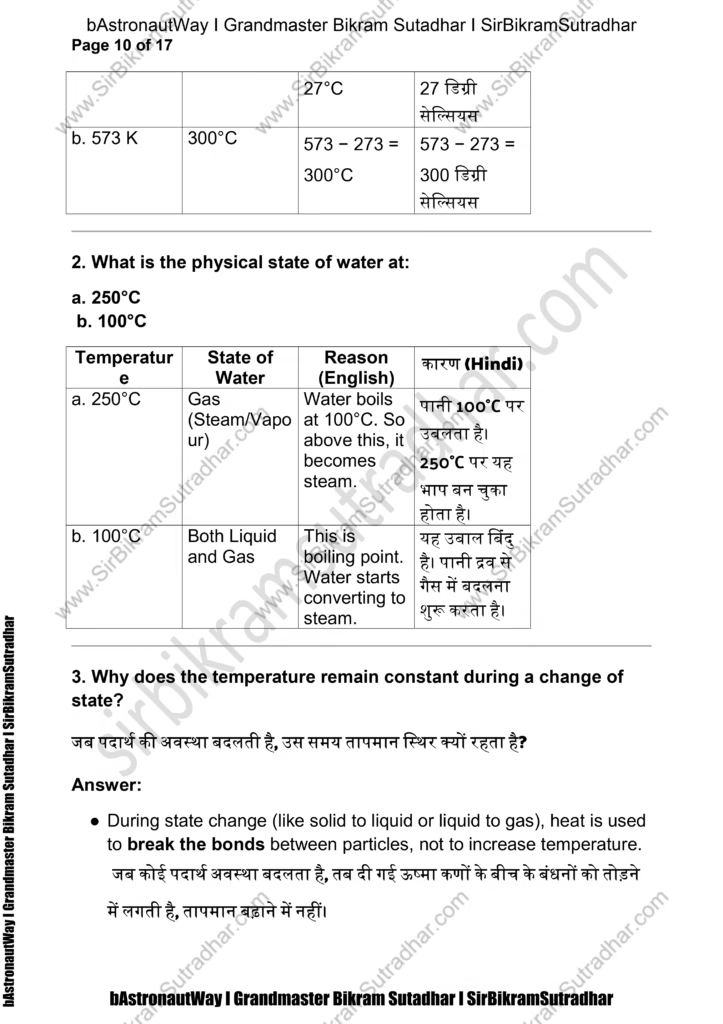
- Give reasons:
(a) A gas fills completely the vessel in which it is kept.
गैस पूरा बर्तन क्यों भर देती है?
● Gas particles move freely in all directions.
गैस के कण सभी दिशाओं में स्वतंत्र रूप से गति करते हैं।
● So they spread and fill the container completely.
इसलिए वे पूरे बर्तन में फैल जाते हैं।
Written By
Full Stack Developer and 5-Time World Record Holder, Grandmaster Bikram Sutradhar
bAstronautWay
SirBikramSutradhar on YouTube
More Story click the link
ICSE CLASS 10 ICSE CLASS 10 BIOLOGY BASTRONAUTWAY SirBikramSutradhar Bikram Sutradhar GrandMaster Bikram Sutradhar selina biology solutions ICSE Biology Selina Solution
class 10 Maths ncert solution.
NCERT Solutions
CBSE Class 10 Mathematics (2025) NCERT Syllabus:
CBSE Class 10 Mathematics NCERT Syllabus (2025) – Chapter-Wise List
CBSE Class 10 Mathematics NCERT Syllabus (2025) – Chapter-Wise List
chapter 4. Quadratic Equations
chapter 5. Arithmetic Progressions
chapter 6. Triangles
chapter 7. Coordinate Geometry
chapter 8. Introduction to Trigonometry
chapter 9. Some Applications of Trigonometry
chapter 11. Areas Related to Circles
chapter 12. Surface Areas and Volumes
class 10 science ncert solution
CBSE Class 10 Science (2025) NCERT Syllabus:
CBSE Class 10 Science NCERT Syllabus (2025) – Chapter-Wise List
CBSE Class 10 Science NCERT Syllabus (2025) – Chapter-Wise List
Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations
Chapter 2 Acids, Bases and Salts
Chapter 3 Metals and Non-metals
Chapter 4 Carbon and its Compounds
Chapter 5 Life Processes
Chapter 6 Control and Coordination
Chapter 7 How do Organisms Reproduce?
Chapter 8 Heredity
Chapter 9 Light – Reflection and Refraction
Chapter 10 The Human Eye and the Colourful World
Chapter 11 Electricity
Chapter 12 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
Chapter 13 Our Environment
📖 Chapter 12 – Organic Chemistry (Selina Textbook)
Table of Contents:
- 12A. Organic Compounds
- 12B. Hydrocarbons: Alkanes
- 12C. Hydrocarbons: Alkenes
- 12D. Hydrocarbons: Alkynes
- 12E. Alcohols
- 12F. Carboxylic Acids
- Exercise 12 MISCELLANEOUS
- Glossary
- Model Question Paper –
📌 Exercise 12 MISCELLANEOUS – Focus Areas:
- 🧬 Consolidated practice from the entire Organic Chemistry chapter
- 🧪 Application-based questions covering alkanes, alkenes, alkynes, alcohols, and carboxylic acids
- 🧾 Writing structural formulas and chemical equations
- 💡 Distinguishing reactions, isomer identification, and conversions
- 📘 Full-syllabus revision to boost conceptual clarity and board exam readiness
Each question in this section is designed to:
- ✅ Strengthen cross-topic understanding
- 📝 Prepare students for application-based and reasoning-based questions
🧠 Improve problem-solving speed and exam performance





